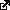Leaking Oil Well Lacked Safeguard Device (the one BP did not
gar - 10.06.2010 02:25
Leaking Oil Well Lacked Safeguard Device (the one BP did not have !!)
The U.S. considered requiring a remote-controlled shut-off mechanism several years ago, but drilling companies questioned its cost and effectiveness, according to the agency overseeing offshore drilling. The agency, the Interior Department's Minerals Management Service, says it decided the remote device wasn't needed because rigs had other back-up plans to cut off a well.
The U.K., where BP is headquartered, doesn't require the use of acoustic triggers.
 http://garizo.blogspot.com/2010/06/leaking-oil-well-lacked-safeguard.html http://garizo.blogspot.com/2010/06/leaking-oil-well-lacked-safeguard.html
The accident has led to one of the largest ever oil spills in U.S. water and the loss of 11 lives. On Wednesday federal investigators said the disaster is now releasing 5,000 barrels of oil a day into the Gulf, up from original estimates of 1,000 barrels a day.
U.S. regulators don't mandate use of the remote-control device on offshore rigs, and the Deepwater Horizon, hired by oil giant BP PLC, didn't have one. With the remote control, a crew can attempt to trigger an underwater valve that shuts down the well even if the oil rig itself is damaged or evacuated.
The efficacy of the devices is unclear. Major offshore oil-well blowouts are rare, and it remained unclear Wednesday evening whether acoustic switches have ever been put to the test in a real-world accident. When wells do surge out of control, the primary shut-off systems almost always work. Remote control systems such as the acoustic switch, which have been tested in simulations, are intended as a last resort.
Nevertheless, regulators in two major oil-producing countries, Norway and Brazil, in effect require them. Norway has had acoustic triggers on almost every offshore rig since 1993.
The U.S. considered requiring a remote-controlled shut-off mechanism several years ago, but drilling companies questioned its cost and effectiveness, according to the agency overseeing offshore drilling. The agency, the Interior Department's Minerals Management Service, says it decided the remote device wasn't needed because rigs had other back-up plans to cut off a well.
The U.K., where BP is headquartered, doesn't require the use of acoustic triggers.
On all offshore oil rigs, there is one main switch for cutting off the flow of oil by closing a valve located on the ocean floor. Many rigs also have automatic systems, such as a "dead man" switch as a backup that is supposed to close the valve if it senses a catastrophic failure aboard the rig
third line of defense, some rigs have the acoustic trigger: It's a football-sized remote control that uses sound waves to communicate with the valve on the seabed floor and close it.
An acoustic trigger costs about $500,000, industry officials said. The Deepwater Horizon had a replacement cost of about $560 million, and BP says it is spending $6 million a day to battle the oil spill. On Wednesday, crews set fire to part of the oil spill in an attempt to limit environmental damage.
Some major oil companies, including Royal Dutch Shell PLC and France's Total SA, sometimes use the device even where regulators don't call for it.
Transocean Ltd., which owned and operated the Deepwater Horizon and the shut-off valve, declined to comment on why a remote-control device wasn't installed on the rig or to speculate on whether such a device might have stopped the spill. A BP spokesman said the company wouldn't speculate on whether a remote control would have made a difference.
Much still isn't known about what caused the problems in Deepwater Horizon's well, nearly a mile beneath the surface of the Gulf of Mexico. It went out of control, sending oil surging through pipes to the surface and causing a fire that ultimately sank the rig.
Unmanned submarines that arrived hours after the explosion have been unable to activate the shut-off valve on the seabed, called a blowout preventer.
 Website: http://garizo.blogspot.com/2010/06/leaking-oil-well-lacked-safeguard.html Website: http://garizo.blogspot.com/2010/06/leaking-oil-well-lacked-safeguard.html
|